“FOBOS” 4π-SPECTROMETER
“FOBOS” 4π-spectrometer is designed for studying of reactions at incident energy of 10-100 AMeV in direct kinematics, i.e. a light projectile impinges upon a heavy target nucleus. The decay of compound-like system from such reactions is characterized by the following products: 1-3 heavy fragments (e.g. fission fragments (FF) or heavy residues (HR)), few intermediate mass fragments (IMF), conventionally defined as being heavier than a -particles but lighter than FF, a fairly large number (10-30) of neutrons and 5-10 light charged particles (LCP). FOBOS is able to register charged reaction products only, from protons up to HR.
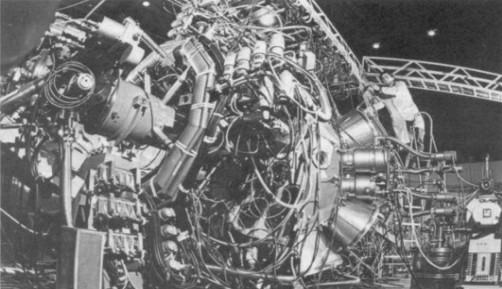
Fig. 1 Spectrometer “FOBOS”
The intention to perform exclusive spectroscopy of charged fragments within a broad dynamic range, covering large intervals of atomic number Z, mass number A, and simultaneously a considerable part of solid angle 4p as well, requires some reasonable compromise between registration efficiency, detector granularity, detection thresholds, possible counting rates etc.. For this purpose, the so-called logarithmic detection principle is applied. This principle assumes a successive increase in the stopping power on the flight path of the particles. This principle has been used in construction of experimental setups such as PAGODA, INDRA (Ganil), FOPI (GSI).
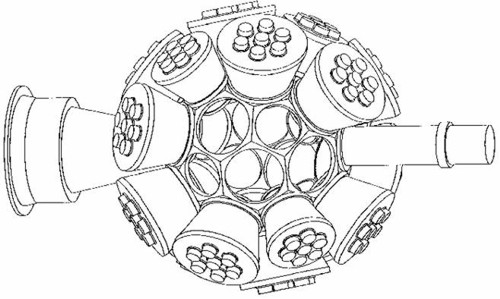
Basic geometry of the spectrometer – a sphere surrounding the target.
Basic geometry of the spectrometer – a sphere surrounding the target. The general lay-out of FOBOS spectrometer is schematically shown in figure. The central vacuum chamber has an inner diameter of 1330 mm. From outside the basic shape is a precisely manufactured 32-face truncated isocahedron with circular holes in the centers of 20 regular hexagonal (d=480 mm) and 10 regular pentagonal (d=380 mm) surface elements for mounting the 20 large and 10 small detector modules, respectively. Two of the opposite placed pentagons of the main geometrical construction are used for the beam entrance and exit.
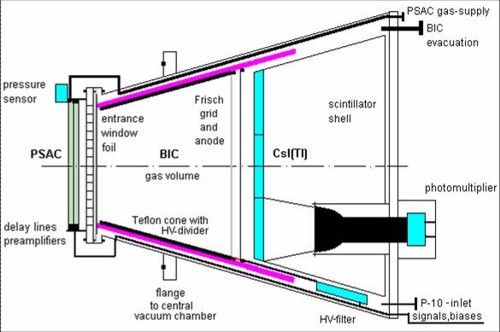
FOBOS spectrometer consists of three consecutive shells
FOBOS spectrometer consists of three consecutive shells of particle detectors and a more granular forward array. One position-sensitive avalanche counter (PSAC), one axial Bragg ionization chamber (BIC), and a mosaic of 7 CsI(Tl) scintillators (CIS) are arranged in 30 separate detector-modules which are mounted to the central vacuum chamber from outside. The sketch of a module is shown in figure. Each five of detector modules are placed axial-symmetrically at the same polar angle with respect to a beam thus forming six detector rings at Ø = 37.380, 63.440, 79.190, 100.810, 116.560 and 142.620.