Upgrade of U-400 cyclotron
- The essential upgrade of U400 cyclotron (U-400R after the upgrade) is one of the subprojects of the “U-400R Accelerator Complex” project. The principal goals of the upgrade are:
-
– increase in the intensity of accelerated beams for ions with A ≈ 50 from 1.2 pμA to 2.5 pμA;
– upgrade of a beam extraction system. The upgraded system will provide beam extraction both with a recharging foil and an electrostatic deflector, which will improve beam quality;
– smooth variation of the beam energy up to 5 times in a wide range of ion mass-to-charge ratios A/Z, which is important for experiments on the dynamics of fusion-fission reactions, MNT reactions, and experiments on nuclear spectroscopy;
– decrease of the energy spread of the beam to 3·10-3;
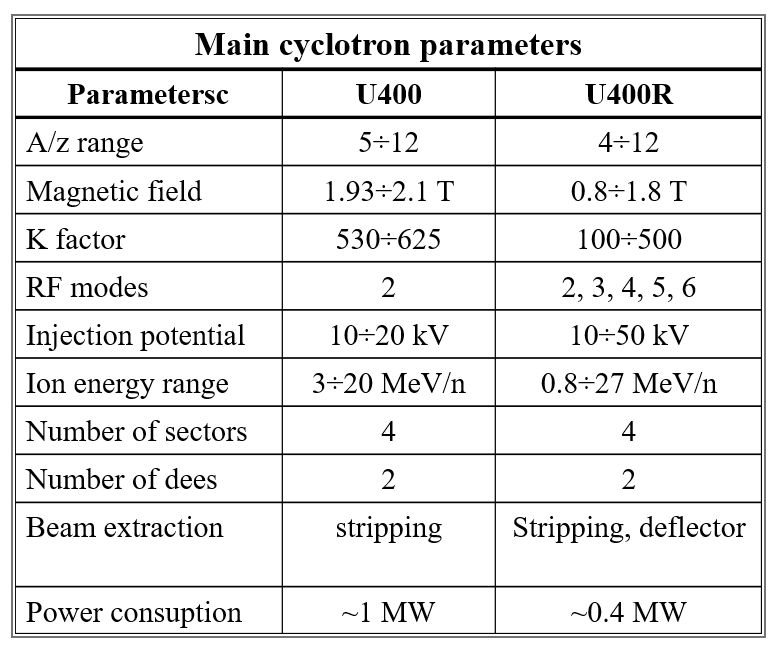
– decrease of the maximum level of the magnetic field in the center of the cyclotron from 1.9 – 2.1 T to 0.8 – 1.8 T, which will significantly reduce the power consumption of the cyclotron and reduce the level of the scattered magnetic field.
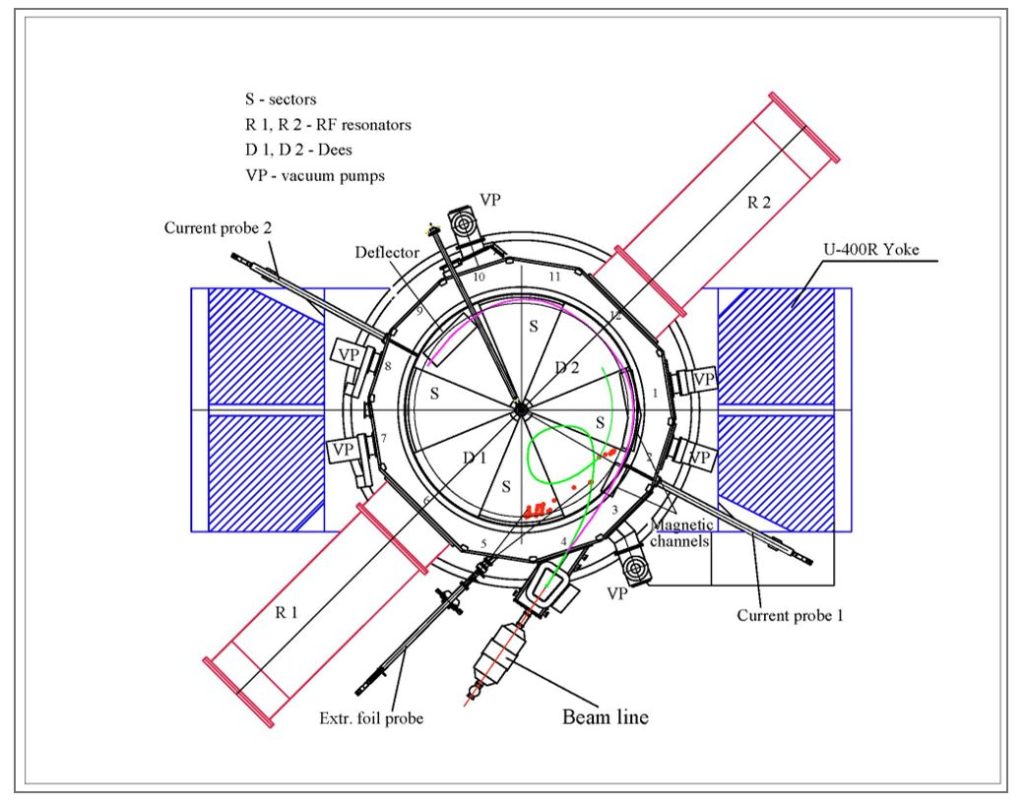
Scheme of the U-400R accelerator
| U400 A/Z=5¸12, E=3¸29 MeV/u | U400R A/Z=4¸12, E=0.8¸27 MeV/u |
| beam | E/A(MeV) | intensity | E/A(MeV) | intensity | Physics |
| 6<A<40 7Li 18O 40Ar | 17 19 5 | 6×1013 2×1013 9×1012 | 17 19 5 | 1×1014 1×1014 3×1013 | production of light RIB, fragmentation, transfer, structure of light exotic nuclei |
| A ~ 60 48Ca 54Cr 58Fe | 5 5 5 | 7.5×1012 4×1012 4.4×1012 | 5 5 5 | 2×1013 6×1012 6×1012 | superheavy elements, spectroscopy of SHE, fusion-fission, quasi-fission, etc. |
| A ~ 150 124Sn 136Xe | 5 5 | 3×1011 5×1011 | 5 5 | 2×1012 3×1012 | DIP, multi-nucleon transfer, new neutron rich nuclei, shell effects |
| A ~ 240 238U | 7 | 3×1010 | 7 | 1011 | neutron-rich SHE, new heavy isotopes, ternary fission, super strong electric fields, e+ e– formation |
The upgraded U-400R accelerator complex will be employed for fulfilling one of the key tasks, i.e., studying deep inelastic multi-nucleon transfer reactions with heavy ions as a novel method for synthesizing new nuclei, with emphasis on neutron-rich nuclei in the N=126 region and on the region of transuranium nuclei.